Details of
The Parents Visa Subclass
At present, all parent permanent residency visa applicants (Subclass 103, 143, 173, 804, 864, 884) must meet these requirements:
- Balance-of-family test (i.e., Applicants must have at least half of the children living in Australia as settled1 citizens or permanent residents).
- Health requirement (i.e., Applicants must not have medical conditions which incur significant healthcare and community service costs).
- Character requirement (i.e., Applicants must not have a criminal record and must not have committed an offence)
- Sponsorship requirement (i.e., Applicants’ Australian children must be committed to be a sponsor by providing accommodation and financial assistance. They must also provide an assurance of support to repay the Australian government any welfare payments made to the visa holder for ten years.)
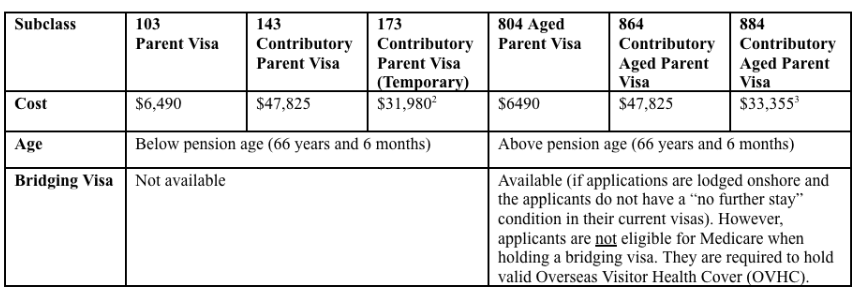
The following table shows the specifics of each visa subclass.
|
Subclass |
103 Parent Visa (Link) |
143 Contributory Parent Visa (Link) |
173 Contributory Parent Visa (Temporary) (Link) |
804 Aged Parent Visa (Link) |
864 Contributory Aged Parent Visa (Link) |
884 Contributory Aged Parent Visa (Temporary) |
|
Cost |
$6,490 |
$47,825 |
$31,9802 |
$6490 |
$47,825 |
$33,3553 |
|
Age |
Below pension age (66 years and 6 months) |
Above pension age (66 years and 6 months) |
||||
|
Bridging Visa |
Not available |
Available (if applications are lodged onshore and the applicants do not have a “no further stay” condition in their current visas). However, applicants are not eligible for Medicare 4 when holding a bridging visa. They are require to hold valid Overseas Visitor Health Cover (OVHC). |
||||
Note: While non-contributory visas (103 and 804) take longer to process (due to their being non-contributory), applicants can opt to switch to contributory visas (143 and 864) and have their original application dates taken into consideration for the queue. However, applicants of parent visas are not allowed to switch to “aged” parent visas. If they do so in order to receive a bridging visa, they will need to withdraw their original applications and forfeit their original application dates.
1. “Settled” means having been a lawful resident in Australia for at least two years.
2. The “temporary” visa is valid for two years. It allows applicants to split the costs of a contributory visa into two instalments. Holders of Visa 173 can apply for Visa 143 when holding the visa and will have Visa 143 granted within a short period of time.
3. The “temporary” visa is valid for two years. It allows applicants to split the costs of a contributory visa into two instalments. Holders of Visa 884 can apply for Visa 864 when holding the visa and will have Visa 864 granted within a short period of time.
4. Except for a limited list of 11 countries that have reciprocal agreements with Australia and therefore are eligible for essential Medicare.
More details
Information about
parents temporary visas
When waiting for their permanent resident visas to be granted, there are currently two temporary visa options for parents. Migrant children have to commit to sponsoring their parents. Applicants have a health requirement and a character requirement. In addition, parents are required to have valid Overseas Visitor Health Cover (OVHC) during their stay. However, both visas have short validity periods and require parents to leave the country before re-applying.
| Subclass | Visa 870 Sponsored Parent (Temporary) Visa (Link) | Visa 600 Visitor Visa (Sponsored Family Stream) (Link) |
| Cost |
$5,090 for up to 3 years $10,180 for up to 4 years |
$145 |
| Cost of sponsorship applications | $420 (In addition, the sponsor must meet the requirement of having a taxable income of $83,454.80 or more). | A security bond may be required. |
| Challenges |
The length of the visas granted varies. Some case officers may grant 3 or 5 years (in accordance to the lengths desired by the applicants). But there are Facebook group members who were only granted for 7 months and one year despite having applied for a three-year visa and having paid $5,090.
Visa holders can stay for a maximum of 10 years. But they must leave the country for at least 90 days before being granted another visa. |
The length of the visas granted varies. Some were granted a three-month visa. Some were granted a 12-month visa over an 18-month period. Visa holders cannot stay longer by extending this visa. They must apply for another visa. |

